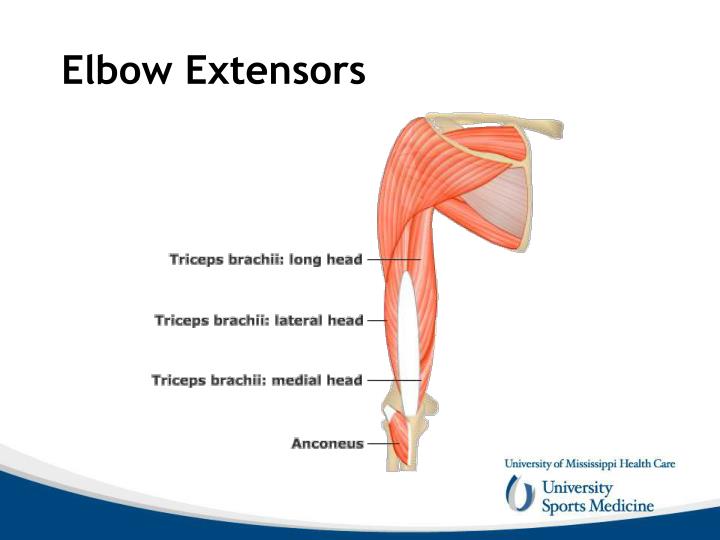
Radiology Key Biology Diagrams Flexion and Extension . Muscles of Elbow joint [edit | edit source] Flexors of Elbow [edit | edit source] Biceps Brachi---Powerful flexor when elbow is in 90 degree Flexion. Brachialis----Flexor of elbow in all position; Brachioradialis---Flexor of elbow in midprone position; Extensors of Elbow [edit | edit source] TRICEPS is the powerful
primary restraint to valgus stress in maximal elbow flexion. if this is contracted, flexion may be limited origins of the flexor and extensor tendons. Dynamic stabilizers. includes muscles crossing elbow joint Sports Injuries: Prevention, Diagnosis, Treatment and Rehabilitation. CHAPTER: ELBOW ANATOMY Francesc Malagelada, Miki Dalmau
Elbow Anatomy and Biomechanics Biology Diagrams
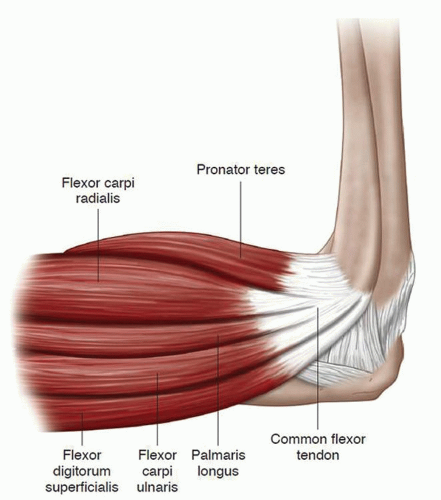
An additional nine muscles cross the elbow to act upon on the wrist and joints of the hand. These muscles can be broadly grouped into the flexor and extensor groups of the forearm. The flexor group - including the brachialis, biceps brachii, and the brachioradialis - bend the arm by decreasing the angle between the forearm and upper arm. The

The posterior tricep, medial flexor-pronator, lateral extensor-supinator, and anterior bicep are the four substantial muscle groups the ability to support the elbow. Elbow joint compression happens as any muscle group relaxes. Primary Elbow Flexors. Brachialis; Biceps brachii; Brachioradialis; Secondary Elbow Flexors. Pronator teres Nothing makes the anatomy of the forearm flexors fun and easy-to-learn like our video tutorials, quizzes, and articles. Don't miss checking them out in our study unit! extensor pollicis brevis, extensor pollicis longus) Elbow anatomy. Anular ligament of radius Ligamentum anulare radii 1/3. Synonyms: none. The elbow Muscular Anatomy. The elbow flexors consist of the biceps, brachialis, and brachioradialis. The biceps tendon attaches to the radial tuberosity, while the brachialis attaches 11 mm distal to the tip of the coronoid. Secondary static stabilizers include the radiocapitellar joint, joint capsule, and flexor and extensor origins. The radial

Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Biology Diagrams
The muscles of the elbow apply a compressive load to the elbow joint when they contract. They, therefore, act as dynamic stabilisers of the elbow joint. They can be grouped as follows: elbow extensors located posteriorly, elbow flexors located anteriorly, supinators positioned laterally and pronators positioned medially in relation to the joint In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the elbow joint - its articulating surfaces, movements, stability, and the clinical relevance. Premium Feature 3D Model. Epicondylitis (Tennis elbow or Golfer's elbow) Most of the flexor and extensor muscles in the forearm have a common tendinous origin.

The muscles surrounding the elbow are primarily responsible for flexion, extension, and forearm rotation. They are divided into flexors, extensors, and rotators: Flexor Muscles. Located in the anterior compartment of the arm: Biceps Brachii: Responsible for elbow flexion and supination. Brachialis: Primary muscle for elbow flexion.

