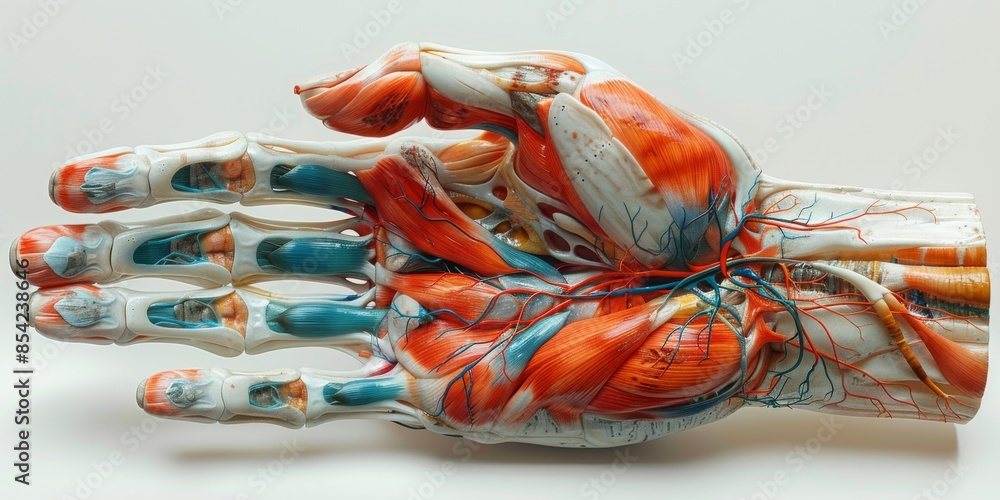
Muscles of the Anterior Hand Superficial View Biology Diagrams The muscles of the hand are the skeletal muscles responsible for the movement of the hand and fingers.The muscles of the hand can be subdivided into two groups: the extrinsic and intrinsic muscle groups. The extrinsic muscle groups are the long flexors and extensors.They are called extrinsic because the muscle belly is located on the forearm.The intrinsic group are the smaller muscles located

A video tutorial that covers the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the hand including actions and innervation.Access my FREE Online Membership today → https Muscles, Extrinsic Muscles, Intrinsic Muscles. What are Intrinsic Muscles. Intrinsic muscles are types of muscles that occur closer to the axial and the appendicular skeleton. For instance, the intrinsic muscles of the hand lay deeper in the hand. Further, the main function of the intrinsic muscles is to control flexion and extension. There are 11 intrinsic muscles and 15 extrinsic muscles in each hand. Names of the Muscles of the Hand and Fingers With Basic Anatomy. Intrinsic Muscles in the Hand. These muscles originate from the hand's bones, ligaments, or fascia, also getting inserted within the hand area. It means these are the muscles that are located in their entirety
Extrinsic Muscles of the Hand Biology Diagrams
The muscles of the hand are responsible for the hand and fingers' movement. The muscles of the hand are redivided into two groups: the extrinsic muscles and the intrinsic muscle groups. The extrinsic groups are the long flexors and extensors muscles. They are termed extrinsic muscles because the muscle belly is positioned on the forearm. The […]

The document provides an overview of the anatomy of the hand. It describes the 27 bones in the hand and wrist, including the carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges. It outlines the extrinsic muscles that flex and extend the wrist and digits, as well as the intrinsic muscles of the hand including the thenar, hypothenar, lumbricals, and interossei The muscles that act on the hand can be divided into two groups: Extrinsic muscles - located in the anterior and posterior compartments of the forearm. They control crude movements and produce a forceful grip. Intrinsic muscles - located within the hand itself. They are responsible for the fine motor functions of the hand. Left: Muscles in the anterior compartment of extrinsic muscles (flexor muscles of the forearm)—The muscles of the anterior compartment of the forearm are depicted in this image from the deepest layer (left) to the most superficial one (right): (a).Pronator quadratus (PQ); (b). Flexor digitorium profundus (FDP); (c). Flexor pollicis longus (FPL); (d).

