Human muscle internal parts anatomy 3d render Biology Diagrams In this article, we will explore the many functions of muscle in the human body as well as its basic structure, types and classifications. Key facts about muscle tissue; Types: Striated muscle (skeletal, visceral striated, cardiac) producing contractions that move body parts, including internal organs. Interestingly, these proteins are not

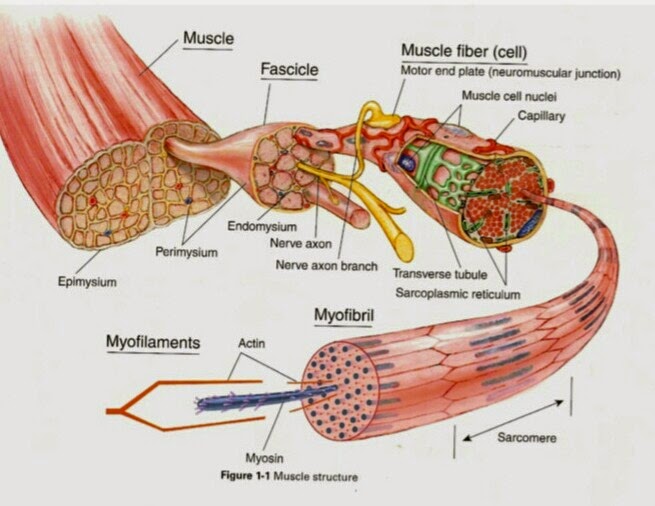
There are three types of muscle in the body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. As with any muscle, the smooth, involuntary muscles of the visceral muscle tissue (which lines the blood vessels, stomach, digestive tract, and other internal organs) are composed of bundles of specialized cells capable of contraction and relaxation to create movement. There are 12 major anatomy systems: Skeletal, Muscular, Cardiovascular, Digestive, Endocrine, Nervous, Respiratory, Immune/Lymphatic, Urinary, Female Reproductive, Male Reproductive, Integumentary. Muscular System The muscular system is responsible for the movement of the human body. These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Skeletal muscles have three layers of connective tissue (called "mysia", singular: "mysium") that enclose it and provide structure to the muscle as a whole, and also compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle (Figure 6.2).

Muscular functions and anatomy Biology Diagrams
The Muscles of the Human Body Muscles are essential components of the human body, enabling movement, maintaining posture, and performing a variety of vital functions. Understanding the structure, properties, and classification of muscles is fundamental for studying human biomechanics, physical activity, and exercise science. General Information About Muscles Muscles are soft tissues composed human muscle system, the muscles of the human body that work the skeletal system, that are under voluntary control, and that are concerned with movement, posture, and balance. Broadly considered, human muscle—like the muscles of all vertebrates—is often divided into striated muscle (or skeletal muscle), smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.Smooth muscle is under involuntary control and is

Muscle tissue is composed of cells that have the ability to shorten/contract in order to produce movement. The muscle cells, also called muscle fibers are long and slender. They are arranged in bundles or layers that are surrounded by connective tissue. Actin and myosin are the main contractile proteins in muscular tissue.

The Muscles of the Human Body Biology Diagrams
Learn about the three types of muscle as you use our 3D models to explore the anatomical structure and physiology of human muscles. And don't worry, we'll explain the naming of skeletal muscles, too. Active muscles break glucoses off of glycogen molecules to provide an internal fuel supply. When muscles run out of energy during either

Human anatomy, a critical foundation of medical science, involves the comprehensive study of the structure of the human body. This section of the 3D Anatomy Atlas provides an interactive exploration of human anatomy in three-dimensional space, offering users a unique and immersive way to understand the complex arrangements of tissues and organs.