Cell Membrane protective layer around all cells Biology Diagrams The Golgi apparatus is a pivotal organelle in eukaryotic cells, playing an essential role in processing and packaging macromolecules. Its significance lies in its ability to modify proteins and lipids, preparing them for their specific functions within the cell or for secretion outside of it.
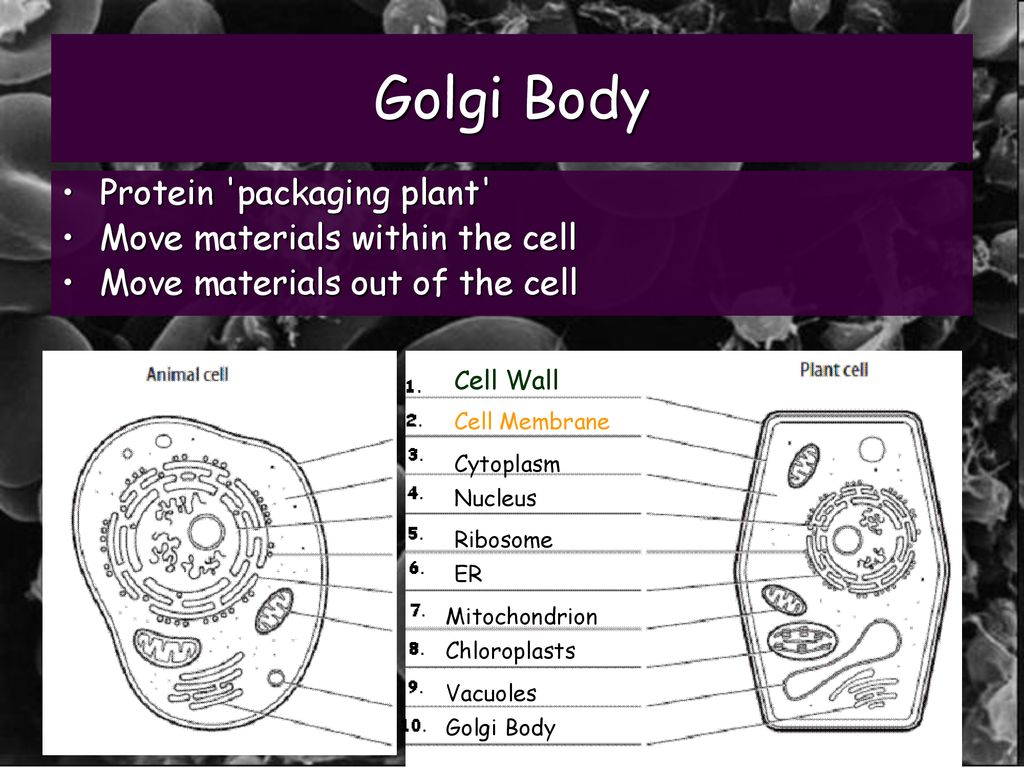
Golgi apparatus, organelle of eukaryotic cells that is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids. The Golgi apparatus is made up of a series of flattened, stacked pouches called cisternae and is located in the cytoplasm near the cell nucleus.
Definition, Structure, Function Biology Diagrams
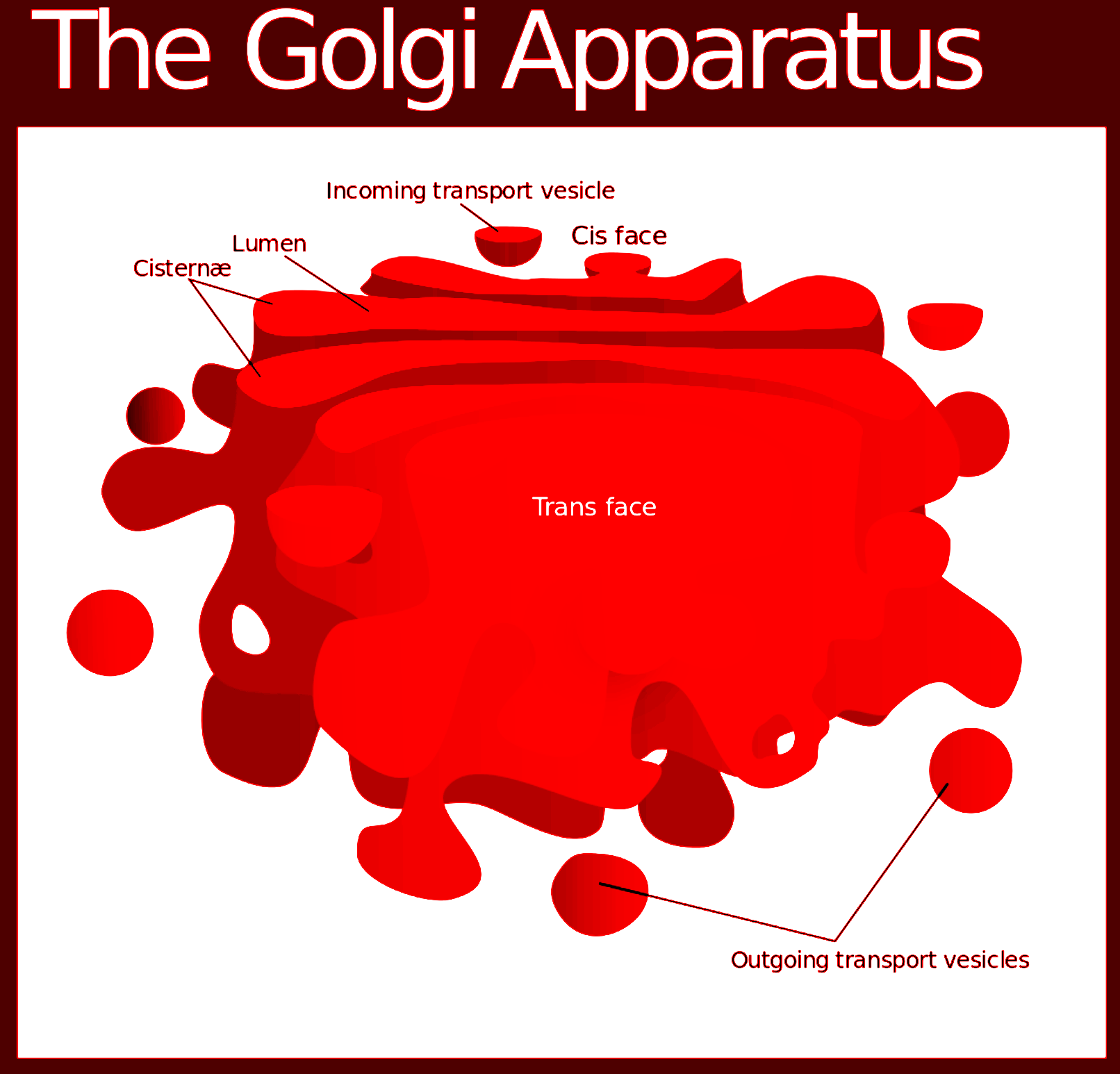
The Golgi apparatus is the central organelle mediating protein and lipid transport within the eukaryotic cell.Typically textbooks illustrate the Golgi as something resembling a stack of pita bread. Key Points: Golgi Apparatus. Definition: The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells responsible for processing, modifying, and packaging proteins, lipids, and other molecules.; Structure: It consists of stacked, flattened membrane sacs (cisternae) and is located near the endoplasmic reticulum and nucleus.Its structure varies across species. This comprehensive review article dives deep into the Golgi apparatus, an essential organelle in cellular biology. to mannose residues present on Factor V and Factor VIII proteins, helping facilitate their packaging into transport neuronal polarity require the activity of protein kinase D in the Golgi apparatus. J. Neurosci. 2008;28:
.jpg)
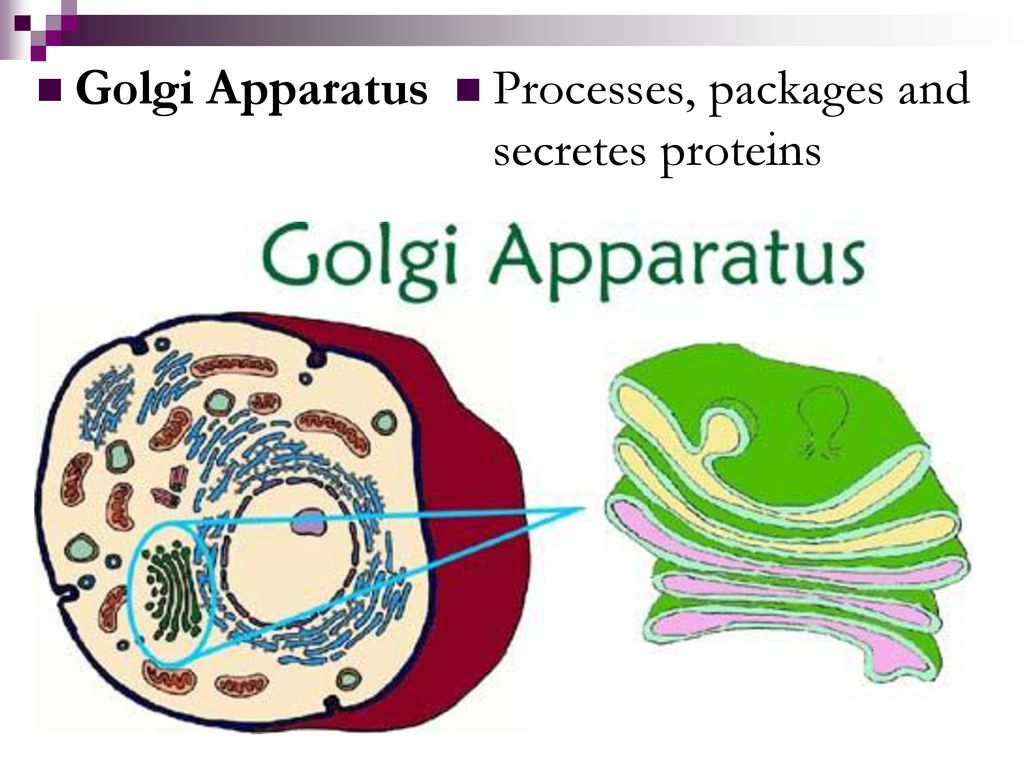
The Golgi apparatus, a complex of flattened membrane-bound sacs, is the primary organelle responsible for modifying and packaging proteins. Within its compartments, proteins undergo glycosylation, sulfation, and phosphorylation, altering their function, stability, and recognition. Additionally, the Golgi packages proteins into vesicles, preparing them for transport to their final destinations

The Golgi Apparatus: Essential for Protein Modifications and Packaging ... Biology Diagrams
This sequential processing is vital for the maturation and functional diversification of proteins. The trans face of the Golgi apparatus, in contrast, is oriented towards the plasma membrane and other cellular destinations. This side is responsible for sorting and packaging proteins into vesicles for transport. Secretion of proteins from eukaryotic cells requires the coordinated function of multiple organelles and cellular machineries. After synthesis and translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum, proteins are exported to the Golgi apparatus, a multi-compartment organelle that is the protein modifying, packaging and distribution center of the secretory pathway.