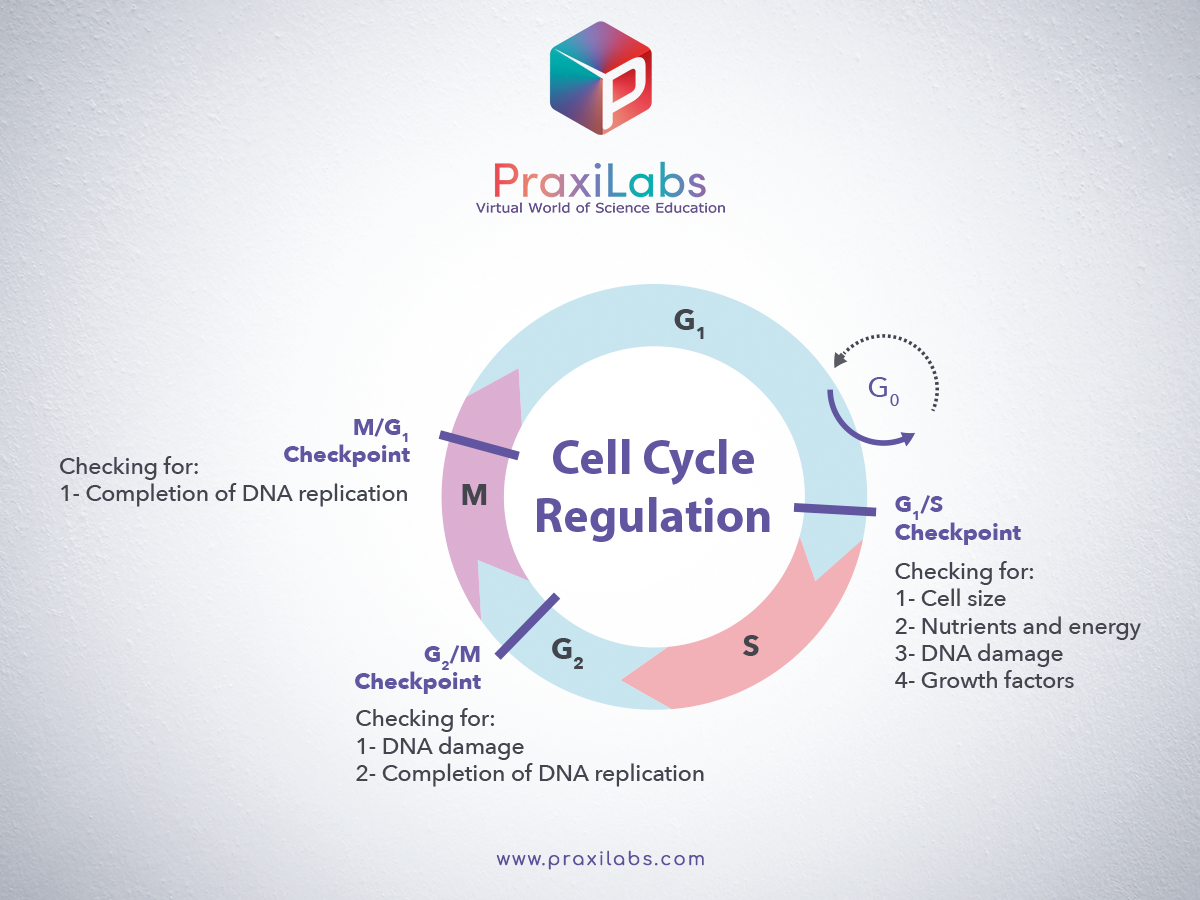
Cell cycle Plant cell Cell division Biology Diagrams Learn about the three main checkpoints in the eukaryotic cell cycle: G1, G2, and metaphase (spindle) checkpoints. Understand how they monitor and regulate the progression of cellular events in response to various conditions.

Learn about the steps and regulation of the cell cycle, a process of growth, replication, and division of cells. Find out how checkpoints ensure the accuracy of DNA and prevent errors that can lead to tumors and cancer.
7.4: Cell Cycle Checkpoints Biology Diagrams
Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle. These include growth to the appropriate cell size, the replication and integrity of the chromosomes, and their Learn about the three major checkpoints in the eukaryotic cell cycle: G1, G2/M, and spindle checkpoints. Find out how they regulate cell cycle progression, DNA replication, and chromosome segregation. Learn about the mechanisms that regulate the cell cycle and prevent abnormal cell division. Explore the roles of cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and checkpoint proteins in controlling the cell cycle phases and responding to DNA damage.
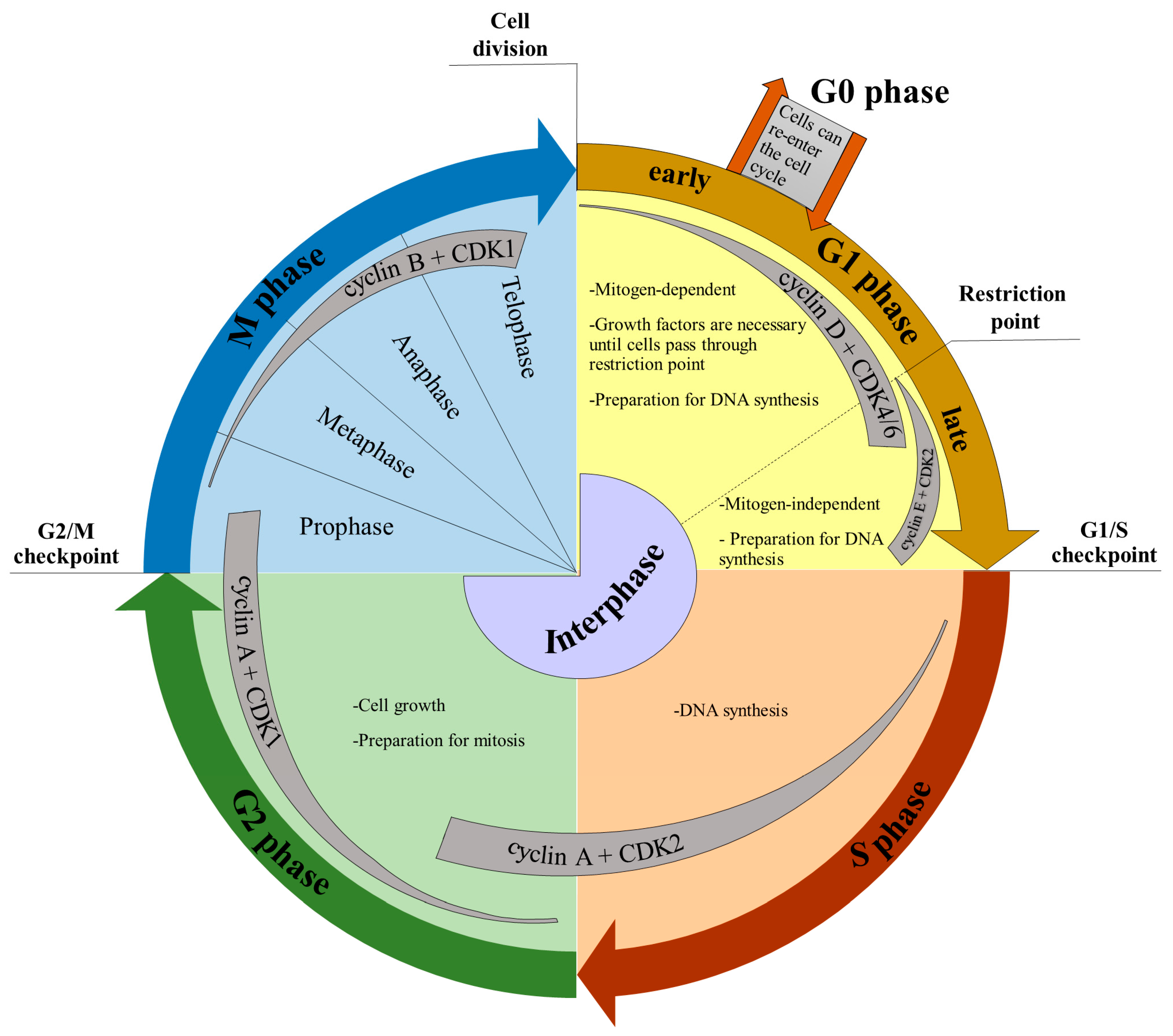
Learn about the cell cycle's stages, mechanisms, and checkpoints that ensure accurate DNA replication and distribution. Explore the roles of cyclins, CDKs, and apoptosis in cellular processes. The cell cycle is meticulously regulated by checkpoints, primarily during the G1, S, and G2 phases. These checkpoints ensure that cells only progress to the next phase when conditions are optimal and all necessary preparations have been made.

G1, G2, Metaphase (Spindle) Checkpoints Biology Diagrams
Learn about the cell cycle, the sequence of events that results in cell growth and division. Find out the phases, regulators, and checkpoints of the cell cycle, and how they differ in eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms.

