African Savanna Food Chain Biology Diagrams Food Chain The producers in this biome are; Star grass, red oat grass and Acadia trees. The primary consumers are, grasshoppers, harvester ants, topi, termites, warthogs, dung beetles, hares, mice, impalas, gazelles, and wildebeest The secondary consumers in the biome are know as, the Pangolin, Aardvark, and the mongoose.
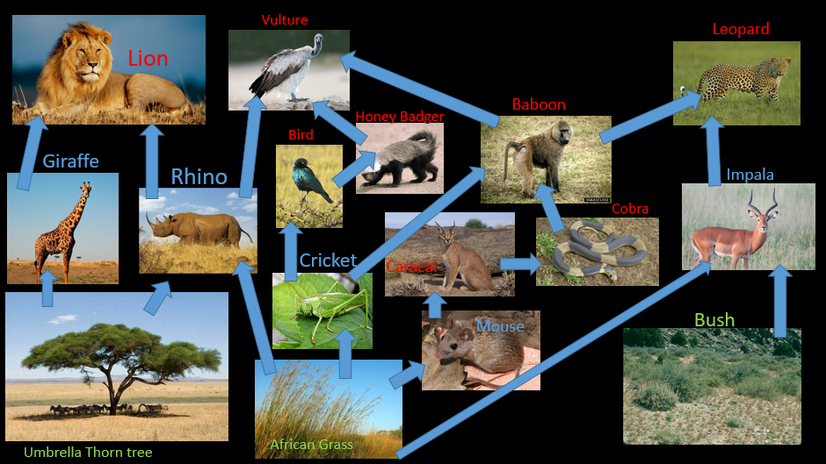
The African food chain, a complex network of relationships between organisms where one organism consumes another for sustenance, is a fascinating example of how these ecosystems thrive. Baboons: These intelligent primates are known for their opportunistic feeding habits, consuming fruits, The Savanna Food Chain. The savanna, a vast This is an African Savanna Food Web.See if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. Look for: The Producers - the trees, shrubs and grass.. The Primary Consumers - the zebras and elephants.. The Secondary Consumers - the cheetah, hyena.. The Scavengers - the termites, vultures and hyena.. The Decomposers or Detritivores - mushrooms

African Food Chain Examples: Exploring the Interconnectedness of Life Biology Diagrams
The main components of the savanna food chain can be divided into producers, primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers, and decomposers. Details of different levels are as below. Producers in the Savanna Food Chain . "Antelope Predation by Nigerian Forest Baboons: Ecological and Behavioural Correlates." The Food Chain. Build a Food Chain Activities; How Nature Works Summary; For Educators: Goals, Objective, & More; Lesson 2: Pollination and Pollinators. The chacma baboon, also known as the Cape baboon, dog-faced monkey, or savanna baboon, is an Afro-Eurasian monkey. One of the largest monkey species, it is found in southern Africa They feed off animals and plants and are often found high on the food chain. Some are top predators. In the Savanna some examples of omnivores are baboons, monkeys and warthogs. Consumer: A consumer is an organism that gets it's food from other organisms. For example Herbivores feed on plants, which cycles the nutrients through the food web.

The olive baboon is also known as the Anubis or savanna baboon and has the widest range in Africa of the 5 baboon species. They are omnivores and mostly feed on fruits, leaves and roots. Meat products such as insects, eggs, small mammals and occasionally carrion are also consumed. Olive baboons will form colonies with intricate social hierarchies. Baboons can change their food sources depending n their proximity to humans. In South Africa, for example, baboons are a menace that will rob you blind. Baboons are known to scale the sides of apartment buildings, checking windows to see if anyone has made the mistake of leaving one unlocked. If they have, the baboons will pry it open, go

Olive baboon facts & info: a guide to the skilled African foragers Biology Diagrams
Olive baboons, sometimes referred to as savanna baboons, survive and thrive in an extreme diversity of habitats. Their range covers 25 countries in central sub-Saharan Africa. They are expert foragers, able to identify food with high nutritional value, and utilizing clever methods to access it. They also have advanced social skills. This

An example of a secondary consumer found in the savanna are baboons. One example of a savanna food chain might show energy flowing from the sun to the grass (producer), then to a zebra

